Explain the Reasons for Different Class of Networks
Class C is a type of IP address that is used for the small network. In this type of network addressing method the first two bits are set to be 1 and the third bit is set to 0 which makes the first 24 bits of the address them and the remaining bit as the host.

Subnet Mask An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
The classes created were based on the network size.

. Jan 25 2021. The host ID is 8 bits long. Dec 26 2019 24 5.
Class B IP addresses - range from 128-191 in the first byte and are designed to be used in medium-sized companies. The IP protocol defines five different address classes. Class C Network.
Although a network server is no more susceptible to failure than any other computer when the files server goes down the entire network may come to a halt. IP address belonging to class C are assigned to small-sized networks. Class B IP address always has its first bits as 10 next 14 bits as a network address and following 16 bits as the host address.
A LinkedIn study found that 80 of professionals consider networking important for their career success. Explain reasons with suitable examples from GCC and Oman in particular. 45 Explain Broadband Baseband and telecommunication services during data transmission.
System Area Network - links high-performance computers with high-speed connections in a cluster configuration. As a result they automatically belong to a different class. Jan 25 2021 6 Dawnofdusk said.
Participating in class discussions is a good way to start meeting other students with whom you share an interest. Up to 24 cash back Storage Area Network - connects servers to data storage devices through a technology like Fibre Channel. Explain its transportation process using a suitable diagram.
Local Area Network LAN Metropolitan Area Network MAN. Why Transportation Safety is of critical importance now a days. This class of IP address is used for a medium network like multinational companies.
Also known as Cluster Area Network. On the basis of inclusions in the law. These are designed to be used in very large companies like Google.
The first bit of the first octet is always set to 0. Unlike Quality of Service QoS traffic management Class of Service technologies. One of the main reasons for this is the different opportunities that you discover through networking which you would have otherwise never seen or thought of before.
Class E is experimental so you can just forget about those too. The first octet of Class C IP address has its first 3 bits set to 110 that is. Thats the reason why our platform was created to network both domestic.
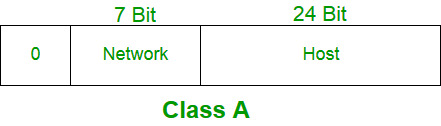
Network addresses for these range from 128 to 191. The idea of an IP class is a convention on where the split between network and host ID occurs. In class A the first bits are reserved for the network address.
If you leave earlier then your class of will be that of a different class. Class C gives 2097152 2 21 Network addresses and 254 2 8-2. The default subnet mask for Class C is 255255255x.
The remaining 21 bits are used to determine network ID. The Network ID has 8 bits. As noted earlier there are many good reasons to attend every class.
Accordingly Class A IP addresses are best used to serve incredibly large networks. This course is dedicated to understanding the fundamentals of carrier packet networks and services and the terminology configuration and operation of specific technologies including Frame Relay and most importantly MPLS. 46 Define simplex half-duplex and full-duplex communication.
But its not enough just to be thereyou need to interact with the the instructor and other students to enjoy a full educational experience. Good network design practices say that critical network services provided by servers should be redundant on the network whenever possible. Choose any one Hazardous items from different class.
The first three classes vary the portion of the address devoted to the network ID and the host ID. The Value of Interaction in Class. Class C IP addresses range from 19200x to 223255255x.
Different criteria are used to classify computer networks. Well begin by understanding the basic structure of a carrier packet network and connecting to it including the Provider. This IP ranges between 192 to 223.
In this class three octets are used to indent the network. In comparison to Class A Class B IP addresses are better suited to serving smaller networks since they reserve 14 bits for a network which leaves only 18 bits for hosts. The default subnet mask for Class A IP address is 255000.
The network ID is 24 bits long. The length of network addresses and host addresses in IP addresses are different in all IP classes. The Class A subnet mask is 255000.
Following are the criteria widely used. Employees who have worked in specific positions or have generally contributed to your business for a longer period are entitled to higher benefits than workers who youve hired more recently. ADVANTAGES OF COMPUTER NETWORKS File Sharing.
The more networks you have the more complex routing tables become. It opens doors to new opportunities. This means that it allows 214 networks and 216 hosts per network.
Class D is for multicast addresses which is something else entirely. Geographical spread Topology Ownership Classification by Geographical Spread Based on geographical spread networks can be classified into the following three categories. The more hosts you have on a single network the more traffic is generated by routine background chatter hosts on the same network find each other by broadcasting to build ARP tables.
43 Explain the difference between different network media Copper Core Fiber-Optic and Wireless. For example for the small number of networks with a very large number of hosts the Class A was created. The remaining 24 bits are available for the host address.
The range of IP addresses is 128000 to 191255255255. 44 Describe the major differences between an analog and digital signal. These are often used where high processing is needed.
A B C D and E. Lol I know this might sound dumb but can you guys explain it better. The Class C was created for numerous networks with small number of hosts.
The 8 bits of host ID is used to determine the host in any network. The Host ID has 24 bits. The higher order bits of the first octet of IP addresses of class C are always set to 110.
In class B the first 16 bits are reserved for the network address while the last 16 bits are. 10 System Area Network. Class A IP addresses - range from 0-127 in the first byte.
Class C IP addresses - range from 192-223 in the first byte and are designed to be used in small-sized companies. A System Area Network is a network that is designed to work in parallel computing environments. Computer clusters make use of System Area Networks to achieve connectivity.
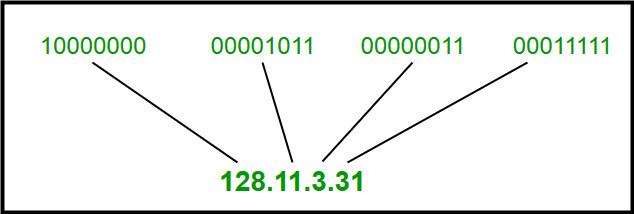
The IP address belonging to Class A uses only the first octet to identify the network and the last three octets are used to identify the host. Explain reasons with suitable examples from GCC and Oman in particular. Sep 29 2019 15 2.
Class B IP address format is. Class of Service CoS is a way of managing traffic in a network by grouping similar types of traffic for example e-mail streaming video voice large document file transfer together and treating each type as a class with its own level of service priority. The system of IP address classes was developed for the purpose of Internet IP addresses assignment.
It connects computers that are in a High Performance Computing setting.
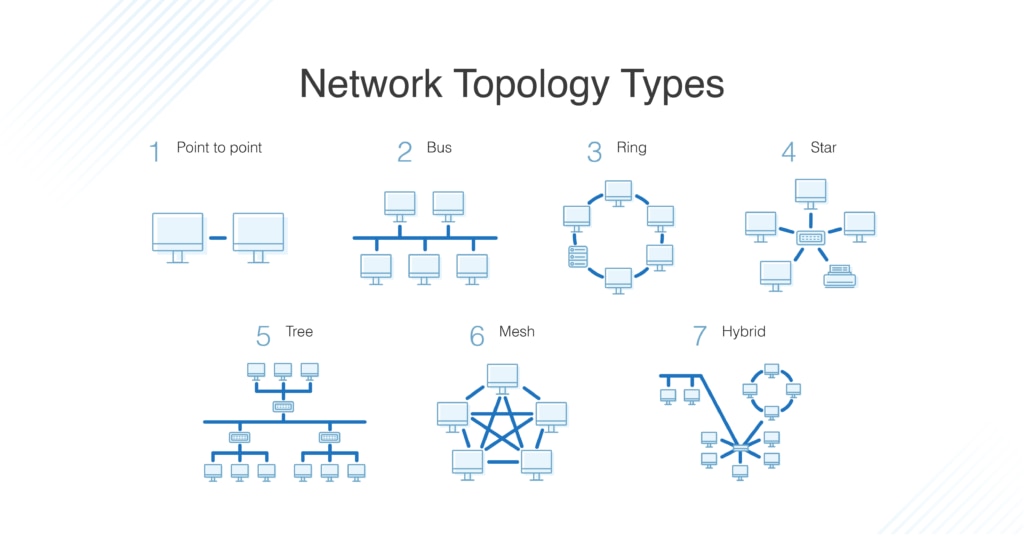
What Is Network Topology Best Guide To Types Diagrams Dnsstuff

The Abcs Of Ip Addresses Pcmag
Basic Ip Addressing And Troubleshooting Guide
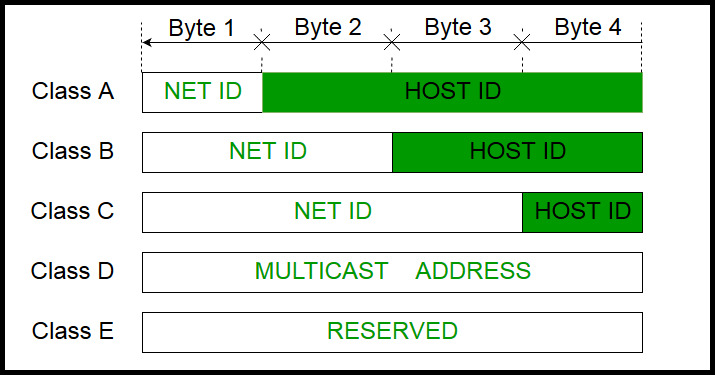
Introduction Of Classful Ip Addressing Geeksforgeeks
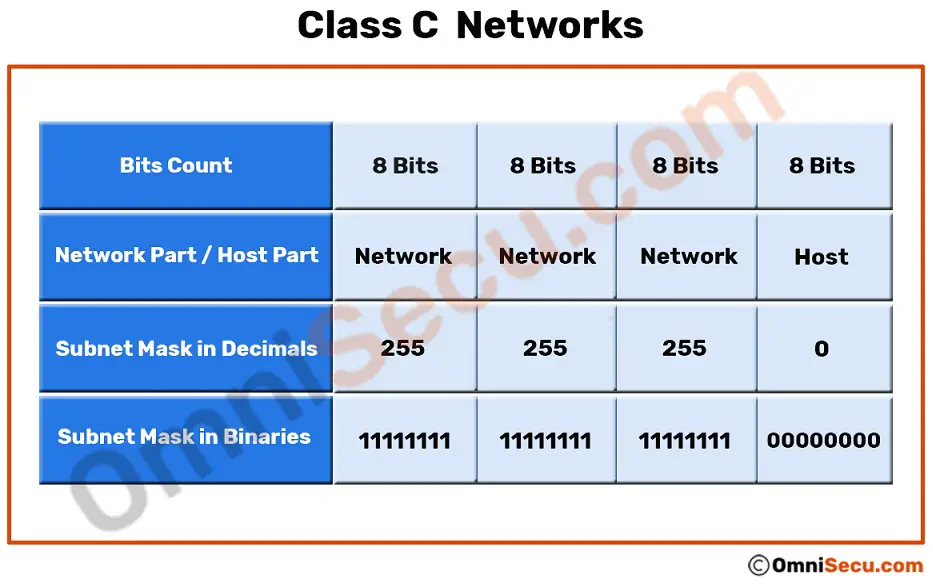
Class C Networks And Class C Ip Addresses
Basic Ip Addressing And Troubleshooting Guide

Introduction Of Classful Ip Addressing Geeksforgeeks
Basic Ip Addressing And Troubleshooting Guide
Subnet And Subnetting Tutorial Guide Dnsstuff

Ip Address Classifications Telecomworld 101
Introduction Of Classful Ip Addressing Geeksforgeeks
Basic Ip Addressing And Troubleshooting Guide
Introduction Of Classful Ip Addressing Geeksforgeeks
Basic Ip Addressing And Troubleshooting Guide




Comments
Post a Comment